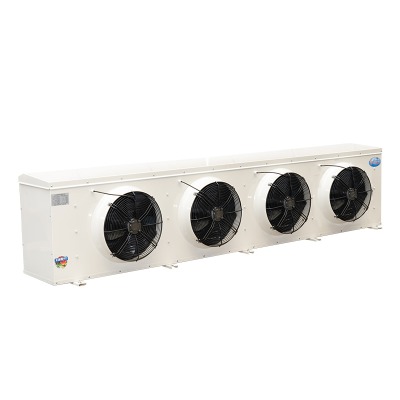
What Are Evaporative Air Coolers? (How They Work & Key Benefits)
Evaporative air coolers (also known as swamp coolers) are energy-efficient cooling devices that use water evaporation to lower air temperature. Unlike traditional air conditioners that rely on refrigerants and compressors, these systems leverage a natural process to provide fresh, cool air—making them an eco-friendly alternative.
How Do Evaporative Air Coolers Work?
The cooling process involves three key steps:
- Water Absorption – A built-in water tank saturates cooling pads.
- Airflow & Evaporation – A fan pulls warm air through the wet pads, causing water to evaporate and absorb heat.
- Cool Air Distribution – The now-cooled air is circulated into the room, reducing temperatures by 5°F to 15°F (3°C to 8°C) depending on humidity levels.
Key Benefits of Evaporative Air Coolers
| Feature | Evaporative Air Coolers | Traditional Air Conditioners |
| Energy Efficiency | Uses 50-75% less electricity | High power consumption |
| Eco-Friendliness | No harmful refrigerants, only water | Uses chemical coolants (e.g., Freon) |
| Ventilation | Brings in fresh outdoor air | Recirculates indoor air |
| Humidity Impact | Adds moisture (ideal for dry climates) | Dehumidifies air |
| Installation Cost | Lower upfront & maintenance costs | Expensive installation & repairs |
Ideal Conditions for Evaporative Cooling
- Best in hot, dry climates (below 60% humidity for optimal performance).
- More effective in well-ventilated spaces (open windows help humid air escape).
- Not suitable for sealed rooms (can increase humidity uncomfortably).
Evaporative air coolers offer a sustainable, cost-effective way to stay cool while reducing energy bills. Their simple design and minimal environmental impact make them a smart choice for eco-conscious users.
Evaporative Air Coolers: The Ultimate Guide to Efficient and Eco-Friendly Cooling
Evaporative air coolers represent a sustainable revolution in cooling technology, offering superior energy efficiency and environmental benefits compared to conventional cooling systems.
Energy Efficiency: How Evaporative Cooling Outperforms Traditional AC
The efficiency advantage of evaporative coolers stems from their simple, refrigerant-free operation:
- Power Consumption Comparison:
- Evaporative coolers use 300-1,200 watts (typical residential units)
- Central AC systems consume 3,000-5,000 watts
- Window AC units require 900-1,500 watts
- Operational Cost Savings:
- Can reduce cooling energy costs by 50-75%
- No compressor means lower peak demand charges
- Minimal maintenance reduces long-term expenses
Environmental Benefits: The Green Cooling Solution
Evaporative technology offers multiple ecological advantages:
- Zero Ozone-Depleting Refrigerants
- Uses only water as cooling medium
- Eliminates risks of refrigerant leaks
- No contribution to global warming potential
- Reduced Carbon Footprint
- Lower energy use directly cuts CO₂ emissions
- Embodied energy in manufacturing is significantly less than AC units
- Sustainable Water Use
- Typical consumption: 3-10 gallons per day
- Advanced models feature water recirculation systems
- Can use gray water in some configurations
Performance Parameters: What to Expect
| Performance Metric | Evaporative Cooler | Traditional AC |
| Temperature Drop Potential | 5-15°F (3-8°C) | 15-25°F (8-14°C) |
| Optimal Humidity Range | Below 60% RH | Any humidity level |
| Air Exchange Rate | Complete air change 2-3x/hour | Recirculates existing air |
| Ventilation Benefits | Constant fresh air intake | Requires separate ventilation |
| Climate Suitability | Best in dry climates | Works in all climates |
Economic Advantages: Long-Term Value Proposition
- Purchase Price: Typically 30-50% less than comparable AC units
- Installation Costs: No need for ductwork or specialized electrical upgrades
- Lifespan: Average 10-15 years with proper maintenance
- Rebate Eligibility: Often qualifies for energy efficiency incentives
Smart Cooling for the Future
The inherent efficiency of evaporative cooling aligns perfectly with global sustainability trends:
- Integrates well with solar power systems
- Complements passive cooling architecture
- Adaptable to smart home automation
- Scalable from personal coolers to industrial applications
For those seeking effective cooling without excessive energy use or environmental impact, evaporative air coolers present a compelling solution that balances performance with planetary responsibility.
Types of Evaporative Air Coolers (Portable, Window, Commercial)
Evaporative cooling technology comes in various configurations to suit different spaces and cooling requirements.
1. Portable Evaporative Coolers
Best for: Homes, offices, and small spaces (up to 500 sq ft)
Key Features:
- Mobility with caster wheels
- Compact, space-saving designs
- Typically 10-25 liter water tanks
- Cooling capacity: 1,000-4,000 CFM
- Power consumption: 100-500W
- Easy plug-and-play operation
Advantages:
- No installation required
- Can be moved room-to-room
- Most affordable option
- Ideal for renters
Limitations:
- • Requires manual refilling (every 4-8 hours)
- • Limited coverage area
- • Louder than stationary units
2. Window-Mounted Evaporative Coolers
Best for: Single rooms (300-800 sq ft)
Key Features:
- Semi-permanent installation
- 15-40 liter water tanks
- Cooling capacity: 3,000-6,000 CFM
- Power consumption: 200-800W
- External water hookup options
Advantages:
- More powerful than portable units
- Saves floor space
- Can be connected to water line
- Better air circulation
Limitations:
- • Requires window installation
- • Not suitable for all window types
- • Limited to one room
3. Commercial/Industrial Evaporative Coolers
Best for: Large spaces (1,000-50,000+ sq ft)
Key Features:
- Roof or wall-mounted installation
- 50-500 liter water capacity
- Cooling capacity: 10,000-50,000+ CFM
- Power consumption: 1,000-5,000W
- Often include ductwork systems
Advantages:
- Covers very large areas
- Most energy-efficient for big spaces
- Can integrate with existing HVAC
- Automated water supply
Limitations:
- • Requires professional installation
- • Higher upfront cost
- • Needs proper ventilation
Comparison Table: Evaporative Cooler Types
| Feature | Portable | Window-Mounted | Commercial |
| Coverage Area | 150-500 sq ft | 300-800 sq ft | 1,000-50,000+ sq ft |
| Water Capacity | 10-25L | 15-40L | 50-500L |
| Airflow (CFM) | 1,000-4,000 | 3,000-6,000 | 10,000-50,000+ |
| Power Usage | 100-500W | 200-800W | 1,000-5,000W |
| Installation | None | Semi-permanent | Permanent |
| Mobility | High | None | None |
| Best For | Small rooms | Bedrooms/living | Warehouses/factories |
Choosing the Right Type
Consider these factors when selecting:
- Space Size: Match cooler capacity to room dimensions
- Usage Duration: Portable for occasional use, commercial for continuous operation
- Climate Conditions: Higher capacity needed for hotter/drier areas
- Ventilation: Commercial units require proper airflow design
- Water Access: Window/commercial models can connect to plumbing
Each type serves distinct purposes, from personal cooling solutions to large-scale industrial applications. The technology scales effectively, maintaining its energy efficiency advantages regardless of size. Modern designs continue to improve portability, water efficiency, and cooling performance across all categories.
How to Choose the Best Evaporative Air Cooler for Your Needs
Selecting the ideal evaporative air cooler requires careful consideration of several technical and environmental factors. As a leading innovator in cooling technology, Zhejiang Jinhao Refrigeration Equipment Co. Ltd recommends evaluating these key aspects to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Key Selection Criteria
- Cooling Capacity (CFM)
- Calculate required CFM: Room volume (cu.ft) × Air changes per hour (typically 20-40) ÷ 60
- Standard recommendations:
- 100-300 sq.ft: 2,000-3,500 CFM
- 300-600 sq.ft: 3,500-6,000 CFM
- 600-1,000+ sq.ft: 6,000-10,000+ CFM
- Water Tank Capacity
- Small units (portable): 10-25 liters (4-8 hour operation)
- Medium units: 25-50 liters (8-12 hour operation)
- Large/commercial: 50-500+ liters (continuous operation)
- Energy Efficiency
- Compare energy consumption per CFM:
- High-efficiency: 0.8-1.2 watts/CFM
- Standard: 1.3-1.8 watts/CFM
- Look for units with variable speed controls
- Compare energy consumption per CFM:
Technical Comparison Table
| Feature | Residential Units | Commercial Units | Industrial Units |
| Coverage Area | 100-800 sq.ft | 800-5,000 sq.ft | 5,000-50,000+ sq.ft |
| Airflow (CFM) | 2,000-8,000 | 8,000-25,000 | 25,000-100,000+ |
| Water Consumption | 3-10 L/hr | 10-30 L/hr | 30-200+ L/hr |
| Power Requirement | 110-240V | 240V/480V | 3-phase 480V |
| Noise Level | 45-60 dB | 55-70 dB | 65-80+ dB |
Climate Considerations
- Ideal for regions with <60% humidity
- In humid climates (60-80% RH), select units with:
- Higher airflow rates
- Advanced cooling media
- Optional dehumidification modes
Special Features to Consider
- Automatic water level control
- Cooling pad quality (aspen vs. synthetic)
- Air filtration options
- Remote control/smart connectivity
- Drainage systems for continuous operation
Zhejiang Jinhao Refrigeration Equipment Co. Ltd emphasizes that proper selection requires balancing these technical specifications with your specific application requirements. Their engineering team recommends consulting with cooling specialists to evaluate:
- Building insulation quality
- Local water quality (mineral content)
- Existing ventilation systems
- Seasonal temperature fluctuations
The company's commitment to developing reliable, innovative cooling solutions ensures customers receive products precisely matched to their operational needs while maximizing energy savings and environmental benefits.



 English
English русский
русский